Spatial audio offers more immersive video consumption experiences to viewers; however, creating and editing spatial audio often expensive and requires specialized equipment and skills, posing a high barrier for amateur video creators. We present MIMOSA, a human-AI co-creation tool that enables amateur users to computationally generate and manipulate spatial audio effects. For a video with only monaural or stereo audio, MIMOSA automatically grounds each sound source to the corresponding sounding object in the visual scene and enables users to further validate and fix the errors in the locations of sounding objects. Users can also augment the spatial audio effect by flexibly manipulating the sounding source positions and creatively customizing the audio effect. The design of MIMOSA exemplifies a human-AI collaboration approach that, instead of utilizing state-of art end-to-end "black-box" ML models, uses a multistep pipeline that aligns its interpretable intermediate results with the user's workflow. A lab user study with 15 participants demonstrates MIMOSA's usability, usefulness, expressiveness, and capability in creating immersive spatial audio effects in collaboration with users.
Users can simply drag the colored overlays and make them overlapped with the actual sounding position of the object to fix the error in 2D positions of the sounding objects.
If the user wants to further fix the depth error, they can move the Z-axis of the sounding object in the 3D object manipulation panel.
Users are able to augment existing audio effect by increasing the relative distance among sounding objects using the sound source overlays.
In the 3D coordinate, users are able to Adjusting the relative position of the sounding objects and the referencing point; move the referencing point and change the moving mode.
Any change made in either panel will automatically trigger the change in other panels to reduce the mental load from the user.
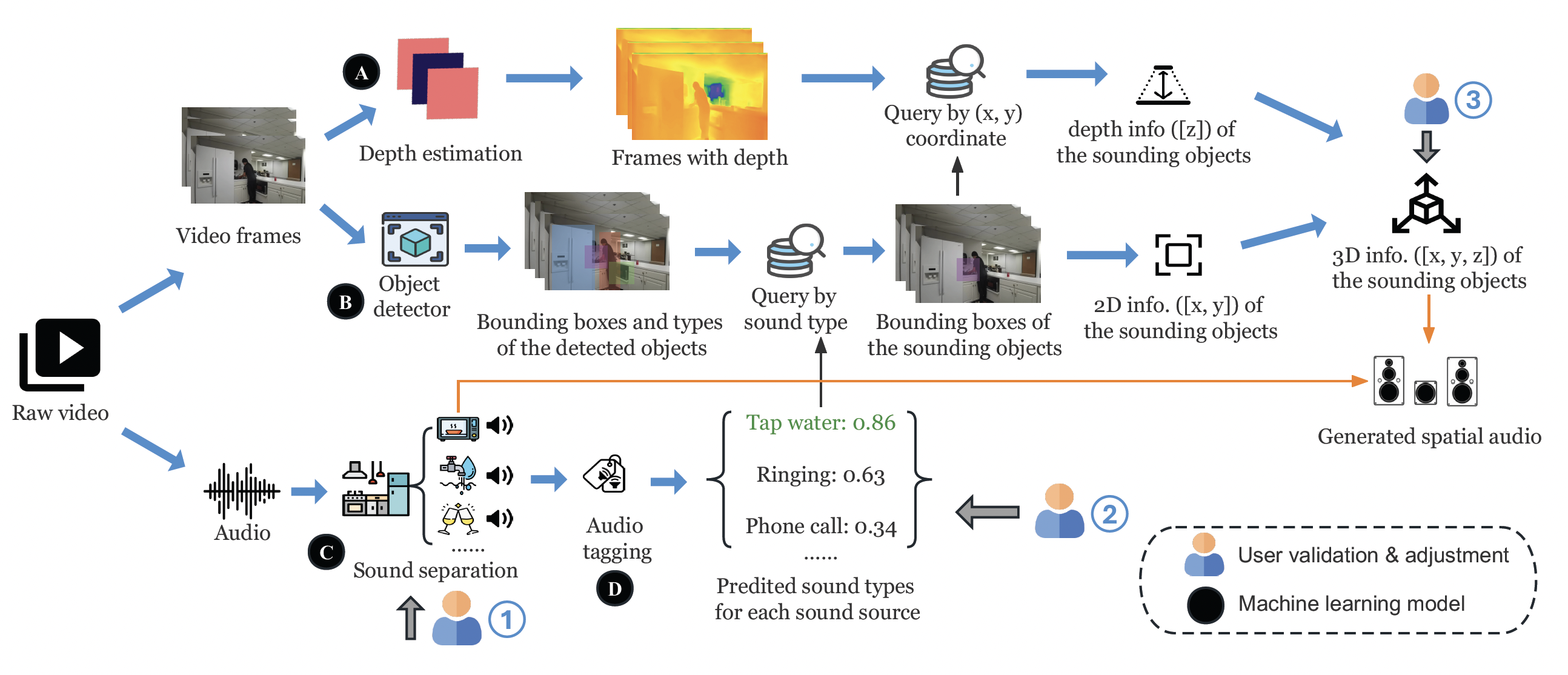
MIMOSA's human-AI collaborative audio spatialization pipeline. Users can validate and adjust the intermediate results in three ways. From left to right, 1: users can adjust the audio properties of each separated soundtrack; 2: users can manually fix the error in aligning the separated soundtrack to the visual object in the video; 3: users can customize the spatial effect for each sounding object by manipulating its corresponding visual position.
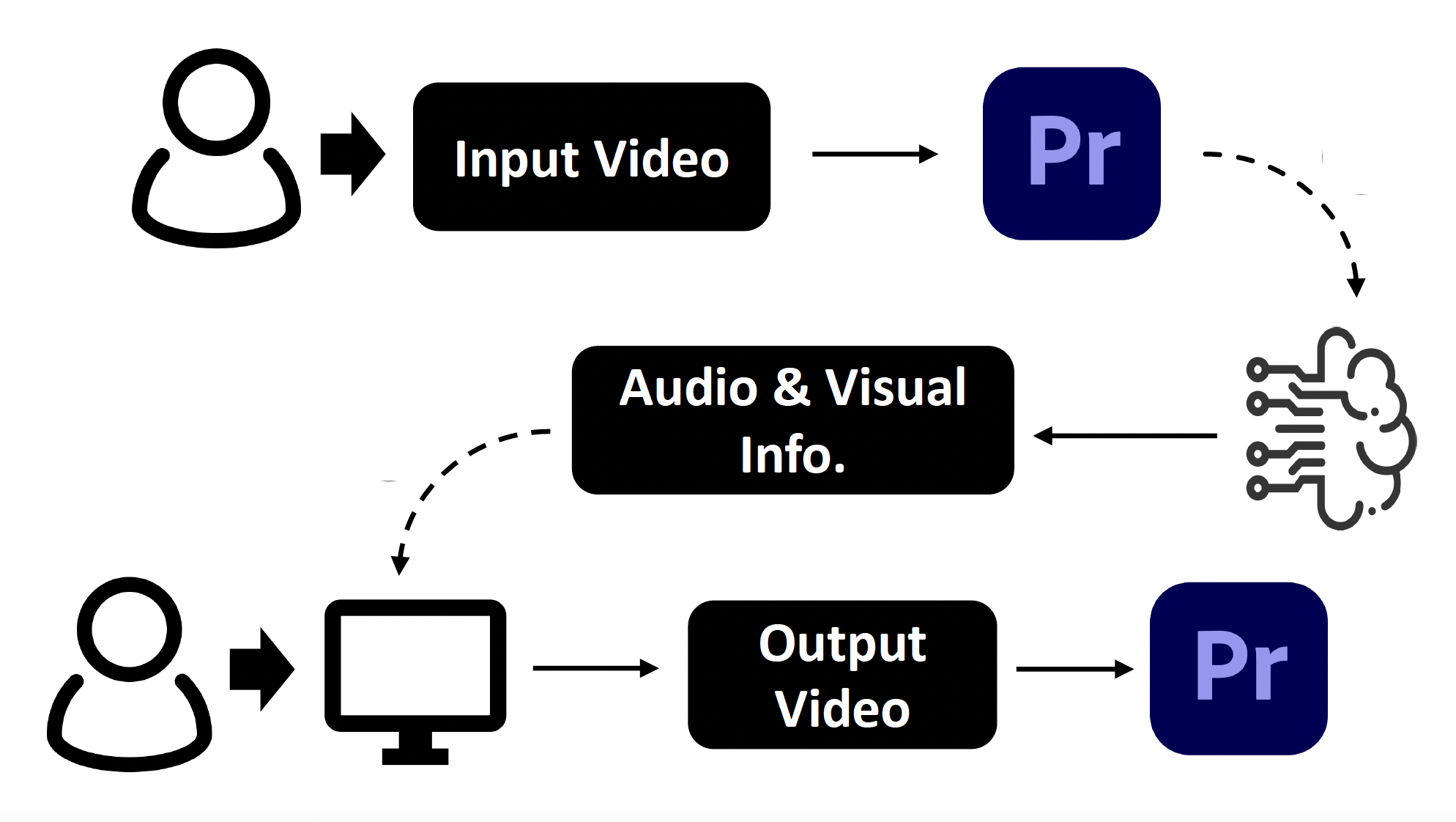
To improve the usability of MIMOSA, we implemented an extension in Adobe Premiere Pro to integrate MIMOSA into the regular workflow of video creators. Users can directly import their video projects and edit the spatial audio effects in the same interface.
@inproceedings{ning2024mimosa,
author = {Ning, Zheng and Zhang, Zheng and Ban, Jerrick and Jiang, Kaiwen and Gan, Ruohong and Tian, Yapeng and Li, Toby Jia-Jun},
title = {MIMOSA: Human-AI Co-Creation of Computational Spatial Audio Effects on Videos},
year = {2024},
isbn = {9798400704857},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3635636.3656189},
doi = {10.1145/3635636.3656189},
booktitle = {Creativity and Cognition},
pages = {156-169},
numpages = {14},
keywords = {creator tools, multimodal, sound effects, video},
location = {Chicago, IL, USA},
series = {C&C '24}
}